TALLY ERP 9
- Payal Mudliar

- Oct 7, 2022
- 24 min read
Updated: Feb 2, 2023

TALLY – An Introduction
Accounting is the process of systematically recording, classifying and summarizing the financial information
It helps individuals and organizations to understand their fiancial health.
It is also known as Book-Keeping & Accountancy
Without cash there is no accountancy.
Accounting वित्तीय जानकारी को व्यवस्थित रूप से रिकॉर्ड करने, वर्गीकृत करने और सारांशित करने की प्रक्रिया है
यह व्यक्तियों और संगठनों को उनके वित्तीय स्थिति को समझने में मदद करता है।
इसे बुक कीपिंग एंड अकाउंटेंसी के नाम से भी जाना जाता है
नकदी के बिना कोई लेखा-जोखा नहीं होता इसीलिए जहाँ पैसा होगा वही एकाउंटिंग होगी ।
Two Types of Accountancy
Manual Accountancy
Computerized Accountancy
Manual Accountancy

Manual Accounting is a system of accounting that uses physical registers and account books, for keeping financial records.
In manual accounting, recording of the transaction can be done through the book of original entry, i.e. journal day book.
मैनुअल एकाउंटिंग accounting की एक प्रणाली है जो वित्तीय रिकॉर्ड रखने के लिए भौतिक रजिस्टरों और खाता पुस्तकों का उपयोग करती है।
मैनुअल एकाउंटिंग में, लेन-देन की रिकॉर्डिंग मूल प्रविष्टि की पुस्तक, यानी जर्नल डे बुक के माध्यम से की जा सकती है।
Advantages
Less expensive to set up.
The risk of corrupted data is much less.
Data loss is less of a risk, particularly if records are stored in a fire-proof environment.
Problems with duplicate copies of the same records are generally avoided.
यह कम खर्चीला होता है ।
डेटा corrupt होने का बहुत कम होता है।
डेटा की हानि का डर कम होता है, खासकर अगर रिकॉर्ड आग में न जले |
समान अभिलेखों की डुप्लीकेट प्रतियों की समस्या से आमतौर पर बचा जा सकता है।
Disadvantages
Time consuming.
Human error.
No backup records in case of loss or damage.
May require specialized knowledge to maintain.
ज्यादा समय खर्च होता है।
त्रुटि की सम्भावना ज्यादा होती है ।
नुकसान या क्षति के मामले में कोई बैकअप रिकॉर्ड नहीं।
बनाए रखने के लिए विशेष प्रकार के ज्ञान की आवश्यकता होती है।
Computerized Accountancy

As its name suggests, "computerized accounting" is accounting done with the aid of a computer.
It tends to involve dedicated accounting software and digital spreadsheets to keep track of a business or client's financial transactions
जैसा कि इसके नाम से पता चलता है, " computerized accounting " एक कंप्यूटर की सहायता से किया जाने वाला accounts है।
इसमें किसी व्यवसाय या ग्राहक के वित्तीय लेन-देन पर नज़र रखने के लिए dedicated accounting software और डिजिटल स्प्रैडशीट का उपयोग किया जाता हैं
Advantages
Simplicity
Reliability
Cost-Effectiveness
Ability to Collaborate
सादगी
विश्वसनीयत
लागत प्रभावशीलता
सहयोग करने की क्षमता
Disadvantages
Potential Fraud
Technical Issues.
Incorrect Information
संभावित धोखाधड़ी
तकनीकी दिक्कतें।
गलत जानकारी
What is Accounting Software?
Accounting Software is an application that helps in storing and managing accounts as well as in performing arithmetic or accounting operations.
अकाउंटिंग सॉफ्टवेयर एक ऐसा एप्लिकेशन है जो खातों के भंडारण याने storage और प्रबंधन याने management के साथ-साथ अंकगणित या लेखा संचालन याने accounting operations करने में मदद करता है।
List of some Famous Accounting Software
Zoho Books
Oracle NetSuite ERP
Vyapar - Accounting & Invoicing
Tally Prime
Busy Accounting Software
Etc.
What is Tally Software?

It is a software for Accounting.
It is provided by Tally Solutions.
It is an standard business accounting software
It handles – accounting, inventory management, tax management, payroll, etc.
यह एक एकाउंटिंग सॉफ्टवेयर है।
इसे टैली सॉल्यूशंस नाम की कंपनी द्वारा प्रदान किया गया है।
यह एक standard business accounting सॉफ्टवेयर है |
यह accounting, inventory management, tax management, payroll, etc. को handle करता है |
Why Tally ?
It is world wide accepted accounting software.
Ex- U.K., India, Indonesia, Bangladesh, etc.
यह विश्व व्यापी स्वीकृत लेखा सॉफ्टवेयर है।
इसे कई देशो में use किया जाता है | जैसे
Who invented TALLY ?
Tally Solutions Pvt.Ltd. Is an Indian Multinational Company provides Tally Software.
Its headquarter is in Bangaluru, Karnataka, India.

Founders :
Mr Shyam Sunder Goenka
Mr Bharat Goenka
It was invented in 1986.
टैली सॉल्यूशंस प्राइवेट लिमिटेड एक भारतीय बहुराष्ट्रीय कंपनी है जो टैली सॉफ्टवेयर प्रदान करती है।
इसका मुख्यालय, भारत के कर्नाटक राज्य के बेंगलुरु में है।
संस्थापक:
श्री श्याम सुंदर गोयनका
श्री मिस्टर भरत गोयनका
इसका आविष्कार 1986 में किया गया था।
Full Form of Tally ERP
Tally Enterprise resource planning software
Versions of Tally Interesting Fact
Tally 4.5 4 + 5 = 9
Tally 5.4 5 + 4 = 9
Tally 6.3 6 + 3 = 9
Tally 7.2 7 + 2 = 9
Tally 8.1 8 + 1 = 9
Tally 9 Tally 9 = 9
Tally ERP 9 Tally ERP 9 = 9
TALLY – Terminology
1. Account
Account is a summarized record of all the transactions relating to every person, every thing or property and every type of service.
खाता प्रकार के सभी लेनदेन का एक संक्षिप्त रिकॉर्ड है।
2. Accounting
It is an art of recording, classifying and summarizing in significant manner and in terms of money, transactions and events which are of financial character and interpreting the results thereof.
Accounting प्रमुख रूप से पैसे के लेनदेन के रिकॉर्ड को रखने, उन्हें वर्गीकृत करने और सारांशित करने की एक कला है जो वित्तीय प्रकृति की होती हैं और उनके परिणामों की व्याख्या करती हैं।
3.Capital:
Capital is the amount invested for starting a business by a person.
पूंजी एक व्यक्ति द्वारा व्यवसाय शुरू करने के लिए निवेश की गई राशि है।
4.Drawings:
Drawings are the amounts withdrawn (taken back) by the Business man from his business for his personal, private and domestic purpose. Drawings may be made in the form cash, goods and assets of the business.
आहरण याने Drawings वह राशि होती है जो व्यवसायी व्यक्ति द्वारा अपने व्यवसाय से अपने व्यक्तिगत, निजी और घरेलू उद्देश्य के लिए निकाली (वापस ली गई) होती है।
5. Capital Expenditure:
Capital expenditures (Cap Ex) are funds used by a company to acquire, upgrade, and maintain physical assets such as property, plants, buildings, technology, or equipment
Capital expenditures (Cap Ex) एक कंपनी द्वारा संपत्ति, पौधों, भवनों, प्रौद्योगिकी, या उपकरण जैसी भौतिक संपत्तियों के अधिग्रहण, उन्नयन और रखरखाव के लिए उपयोग की जाने वाली धनराशि है।
6. Shares:
In simple terms, a share is a percentage of ownership in a company or a financial asset. Investors who hold shares of any company are known as shareholders.
सरल शब्दों में, एक शेयर किसी कंपनी या वित्तीय संपत्ति में स्वामित्व का प्रतिशत है। किसी भी कंपनी के शेयर रखने वाले निवेशकों को शेयरधारक के रूप में याने shareholders के रूप में जाना जाता है।
7. Equity Share Capital:
A company raises capital by offering shares is known as equity share capital or share capital.
शेयरों की पेशकश करके एक कंपनी जो पूंजी जुटाती है उसे इक्विटी शेयर पूंजी या शेयर पूंजी के रूप में जाना जाता है।
8. Preferential share capital:
The capital that a company raises through the issuance of preference shares is termed as preference share capital.
प्रेफरेंस शेयर इक्विटी शेयरों का एक प्रकार हैं.| प्रेफरेंस शेयर रखने वाले निवेशक इक्विटी शेयर होल्डर से अधिक सुरक्षित होते हैं. इसकी वजह है कि अगर कभी कंपनी दिवालिया होने के कगार पर हो तो इस प्रकार के शेयरधारकों को सामान्य इक्विटी शेयरधारकों के मुकाबले पूंजी के भुगतान में वरीयता दी जाती है.
9. Business transaction
A business transaction is an exchange of values between two parties
एक व्यापार दो पक्षों के बीच मूल्यों के आदान-प्रदान को "व्यावसायिक लेनदेन" के रूप में जाना जाता है।
10. Purchase
A purchase means goods purchased by a businessman from suppliers.
खरीद का अर्थ है एक व्यापारी द्वारा आपूर्तिकर्ताओं याने suppliers से खरीदा गया सामान।
11. Sales:
Sales is goods sold by a businessman to his customers.
बिक्री एक व्यापारी द्वारा अपने ग्राहकों को बेची जाने वाली वस्तु है।
12. Purchase Return or Rejection in or Outward Invoice
Purchase return means the return of the full or a part of goods purchased by the businessman to his suppliers.
Purchase Return का अर्थ है व्यवसायी द्वारा अपने आपूर्तिकर्ताओं को खरीदे गए माल का पूरा या कुछ भाग वापस करना।
13. Sales Return or Rejection out or Inward Invoice
Sales return means the return of the full or a part of the goods sold by the customer to the businessman.
Sales return का अर्थ ग्राहक द्वारा व्यवसायी को बेचे गए माल के पूर्ण या आंशिक भाग की वापसी से है।
14. Assets
Assets are the things and properties possessed by a businessman not for resale but for the use in the business.
संपत्ति वे चीजें और संपत्तियां हैं जो एक व्यवसायी के पास पुनर्विक्रय याने resale के लिए नहीं बल्कि व्यवसाय में उपयोग के लिए होती हैं।
15. Liabilities:
All the amounts payable by a business concern to outsiders are called liabilities.
किसी व्यावसायिक संस्था द्वारा बाहरी व्यक्तियों को देने वाली सभी राशियाँ Liabilities कहलाती हैं।
16. Debtors
Debtor is the person who owes amounts to the businessman.
वे व्यक्ति, संस्था, फर्म, कम्पनी या निगम, आदि जिनसे धन वसूलना रहता है, उन्हें देनदार (Debtor) कहा जाता है।
17. Creditor
Creditor is the person to whom amounts are owed by the Business man.
Creditor व्यक्ति, बैंक, या अन्य उद्यम होते हैं, जिन्होंने किसी अन्य पार्टी को पैसा या ऋण दिया है। जिस पार्टी को क्रेडिट दिया गया है वह कर्जदार है। मान लें कि एक कंपनी बैंक से पैसे उधार लेती है तो कंपनी Debtor हो गइ और बैंक Creditor हो गया
18. Sundry Creditor:
A person who gives goods or services to the business in credit or does not receive the payment immediately from the business and is liable to receive the payment from the business in future is called a Sundry Creditor.
एक व्यक्ति जो व्यापार को सामान या सेवाएं क्रेडिट में देता है या व्यापार से तुरंत भुगतान प्राप्त नहीं करता है और भविष्य में व्यवसाय से भुगतान प्राप्त करने के लिए उत्तरदायी होता है, उसे Sundry Creditor कहते है।
19. Sundry Debtor
A person who receives goods or services from a business in credit or does not make the payment immediately and is liable to pay the business in the future is called a Sundry Debtor.
एक व्यक्ति जो किसी व्यवसाय से क्रेडिट में सामान या सेवाएं प्राप्त करता है या तुरंत भुगतान नहीं करता है और भविष्य में व्यापार का भुगतान करने के लिए उत्तरदायी है, उसे Sundry Debtor कहते है।
20. Debit
The receiving aspect of a transaction is called debit or Dr.
लेन-देन में पैसे प्राप्त करने वाले पहलू को डेबिट या Dr कहते है
21. Credit:
The giving aspect of a transaction is called credit or Cr.
लेन-देन में पैसे देने वाले पहलू को डेबिट या Dr कहते है
22. Secured Loan:
A secured loan is a type of loan in which a borrower pledges an asset such a car, property, equity, etc. against that loan
A secured loan एक प्रकार का ऋण है जिसमें एक उधारकर्ता उस ऋण के लिए एक संपत्ति जैसे कार, घर, अपने शेयर्स आदि को गिरवी रखता है
23. Unsecured Loan
Unsecured loans don't require the borrower to put down any security deposit or collateral. Instead, borrowers are approved by lenders based on personal credit history and income
बिना किसी प्रकार के सुरक्षा गारंटी के दिये जानेवाले लोन को Unsecured Loan कहते हैं। यहाँ कोई Security नहीं होती है तथा यह कर्ज लेने वाले व्यक्ति की वित्तीय स्थिति को देखकर ही लोन दिया जाता है जहाँ कोई संपत्ति आपको गिरवी नहीं रखनी पड़ती है।
24. Revenue Expenditure:
Revenue expenditures are short-term expenses used in the current period or typically within one year.
विभिन्न सरकारी विभागों और सेवाओं पर खर्च, ऋण पर ब्याज की अदायगी और सब्सिडियों पर होने वाले व्यय को राजस्व व्यय कहते हैं। राजस्व व्यय करों, शुल्कों, फ़ीसों, जुर्माना आदि प्रकार की मदों से किए जाते हैं।
25. Bills Payable
Bills payable refers to the indebtedness of a person or business.
जब कोई कंपनी अपनी क्रेडिट पर कोई माल खरीदती है उसका भुगतान अल्प अवधि में करना होता है तो उसे देय खाता यानी अकाउंट्स पेएबल (Accounts Payable) कहते हैं।
26. Bills Receivable:
A bill receivable is a document that your customer formally agrees to pay at some future date (the maturity date).
Bills Receivable एक दस्तावेज है जिसे आपका ग्राहक औपचारिक रूप से भविष्य की किसी तारीख पर भुगतान करने के लिए सहमत होता है।
27. Goods:
Goods are tangible items that can be used and stored. Businesses make goods and sell them to customers, who then own them.
जिन वस्तुओं का कोई व्यापारी व्यापर करता है, वह उसका माल (Goods) कहलाता है, जैसे - यदि कोई व्यापारी गेहूँ का व्यापर करता है तो गेहूँ उसका माल कहलाएगा। यदि फर्नीचर का व्यापार करता है तो फर्नीचर उसका माल कहलाएगा। तो हम इसे ऐसे भी कह सकते है कि जब किसी वस्तु का निर्माण या क्रय, बिक्री करने के उद्देश्य से होता है तो वह माल कही जाती है।
28. Opening Stock:
The amount and value of products or materials that a company has available for sale or use at the beginning of an accounting period: This year's opening stock was, in fact, last year's closing stock.
एक लेखा अवधि की शुरुआत में एक कंपनी के पास बिक्री या उपयोग के लिए उपलब्ध उत्पादों या सामग्रियों की मात्रा और मूल्य: इस साल का शुरुआती स्टॉक, वास्तव में, पिछले साल का समापन स्टॉक था।
29. Closing Stock:
Closing Stock is an amount of unsold stock lying in your business on a given date. In simple words, it's the inventory which is still in your business waiting to be sold for a given period. The closing stock can be in various forms such as raw materials, in-process goods (WIP) or finished goods.
क्लोजिंग स्टॉक एक निश्चित तिथि पर आपके व्यवसाय में बिना बिके स्टॉक की राशि है। सरल शब्दों में, यह वह इन्वेंट्री है जो अभी भी आपके व्यवसाय में एक निश्चित अवधि के लिए बेचे जाने की प्रतीक्षा कर रही है। क्लोजिंग स्टॉक कच्चे माल, इन-प्रोसेस गुड्स (WIP) या तैयार माल जैसे विभिन्न रूपों में हो सकता है।
30. Surplus
A surplus describes the amount of an asset or resource that exceeds the portion that's actively utilized. A surplus can refer to a host of different items, including income, profits, capital, and goods.
Surplus एक संपत्ति या संसाधन की मात्रा का वर्णन करता है जो उस हिस्से से अधिक है जो सक्रिय रूप से उपयोग किया जाता है। व्यवसाय में लगने वाली कोई भी वस्तु Surplus हो सकती है जैसे items, including income, profits, capital, and goods.
31. Depreciation:
The monetary value of an asset decreases over time due to use
किसी संपत्ति का मौद्रिक मूल्य उपयोग के कारण या समय के साथ घटता जाता है
32. Expense:
An expense is the cost of operations that a company incurs to generate revenue. Common expenses include payments to suppliers, employee wages, factory leases, and equipment depreciation.
एक व्यय संचालन की लागत है जो एक कंपनी राजस्व उत्पन्न करने के लिए करती है। सामान्य खर्चों में आपूर्तिकर्ताओं को भुगतान, कर्मचारी वेतन, कारखाने के पट्टे और उपकरण मूल्यह्रास शामिल हैं।
33. Incomes:
Income is the revenue a business earns from selling its goods and services or the money an individual receives in compensation for his or her labor, services, or investments.
आय वह राजस्व है जो एक व्यवसाय अपने सामान और सेवाओं को बेचकर कमाता है या वह धन जो एक व्यक्ति अपने श्रम, सेवाओं या निवेश के मुआवजे में प्राप्त करता है।
34. Solvent:
A company is considered solvent if the realizable value of its assets is greater than its liabilities.
एक कंपनी को Solvent माना जाता है यदि उसकी संपत्ति का वसूली योग्य मूल्य उसकी liabilities. से अधिक है।
35. Insolvent:
A company is considered insolvent if the realizable value is lower than the total amount of liabilities.
एक कंपनी को Insolvent माना जाता है यदि वसूली योग्य मूल्य liabilities की कुल राशि से कम है।
36. Baddebt:
Bad debt is an expense that a business incurs once the repayment of credit previously extended to a customer is estimated to be uncollectible and is thus recorded as a charge off
उधार बिक्री की वह राशि जिसका वसूल होना विभिन्न कारणों से सम्भव नहीं है, डूबत ऋण याने Baddebt कहलाता हैI इसे अप्राप्त ऋण भी कहते हैं
37. Discount Allow:
A discount allowed is when the seller of goods or services grants a payment discount to a buyer
Discount Allow तब होता है जब सामान या सेवाओं का विक्रेता खरीदार को payment discount देता है
38. Discount Receive:
A discount received is the reverse situation, where the buyer of goods or services is granted a discount by the seller.
Discount Receive विपरीत स्थिति है, जहां विक्रेता द्वारा माल या सेवाओं के खरीदार को छूट दी जाती है।
39. Cash Discount:
Cash discounts refer to an incentive that a seller offers to a buyer in return for paying a bill before the scheduled due date.
नकद छूट याने Cash Discount एक प्रोत्साहन को संदर्भित करता है जो एक विक्रेता एक खरीदार को निर्धारित देय तिथि याने scheduled due date से पहले बिल का भुगतान करने के बदले में प्रदान करता है।
40. Trade Discount:
A trade discount is the amount by which a manufacturer reduces the retail price of a product when it sells to a reseller
एक व्यापार याने Trade Discount छूट वह राशि है जिसके द्वारा एक manufacturer अपने product को एक reseller को बेचते समय उसके retail price को कम कर देता है
41. Bank OCC account (Over Credit account):
Open cash credit (OCC) Account is a kind of bank account which basically serves to small & medium enterprises (SME). An OCC A/c holder can have cash credit facility against his stocks & receivables. ... In a majority of cases, the OCC limit is calculated depending upon turnover of the SME.
ओपन कैश क्रेडिट (ओसीसी) खाता एक प्रकार का बैंक खाता है जो मूल रूप से small & medium enterprises (SME) के लिए कार्य करता है। एक ओसीसी खाता धारक के पास अपने stocks & receivables के against में cash credit की सुविधा हो सकती है। अधिकांश मामलों में, एसएमई के टर्नओवर के आधार पर ओसीसी सीमा की गणना की जाती है।
42. Bank OD account (Overdraft account):
It is a type of account in which you can withdraw amount even if there is no fund in your account. The bank sanctions a specific limit and your account can go in negative up to that limit. You have to pay interest only on the amount taken as loan.
यह एक प्रकार का खाता है जिसमें आप अपने खाते में धन न होने पर भी राशि निकाल सकते हैं। बैंक एक specific limit को मंजूरी देता है और आप उस सीमा तक लोन ले सकते है। लोन के रूप में ली गई राशि पर ही आपको ब्याज देना होता है ।
43. Debenture:
A debenture is a type of debt instrument that is not backed by any collateral and usually has a term greater than 10 years.
एक डिबेंचर एक प्रकार का ऋण साधन याने debt instrument है जो किसी भी collateral द्वारा समर्थित नहीं है और आमतौर पर इसकी अवधि 10 वर्ष से अधिक होती है।
44. Bankrupt:
A person judged by a court to be insolvent, whose property is taken and disposed of for the benefit of their creditors.
एक व्यक्ति को अदालत द्वारा दिवालिया घोषित किया जाता है, जिसकी संपत्ति उनके लेनदारों के लाभ के लिए ली जाती है और उनका निपटान किया जाता है।
45. GST:
The goods and services tax (GST) is a value-added tax levied on most goods and services sold for domestic consumption
The goods and services tax (GST) घरेलू उपभोग के लिए बेची जाने वाली अधिकांश वस्तुओं और सेवाओं पर लगाया जाने वाला value-added tax है।
46. CGST:
CGST stands for Central Goods and Services Tax. It subsumes all the taxes that were earlier applicable as central indirect taxes. They are levied by the central government for intrastate movement of goods and services.
CGST का मतलब Central Goods and Services Tax है। यह उन सभी taxes को समाहित करता है जो पहले central indirect taxes के रूप में लागू होते थे। वे केंद्र सरकार द्वारा वस्तुओं और सेवाओं की अंतर्राज्यीय आवाजाही याने intrastate movement के लिए लगाए जाते हैं।
47. SGST:
SGST is levied by the state government on intra-state goods and service transactions SGST subsumes earlier taxes such as VAT, entertainment tax, luxury tax, Octroi,etc.
SGST राज्य सरकार द्वारा राज्य के भीतर goods और service transactions पर लगाया जाता है SGST VAT, entertainment tax, luxury tax, Octroi, आदि जैसे पुराने taxes को समाहित करता है।
48. UTGST:
Similar to how SGST is levied by the state governments on the intra-state supply of goods and services, Union Territory Goods and Services Tax or UTGST is levied by the Union Territory governments.
जिस तरह से राज्य सरकारों द्वारा SGST लगाया जाता है, उसी तरह केंद्र शासित प्रदेशो में सरकारों द्वारा Union Territory Goods and Services Tax याने UTGST लगाया जाता है।
49. IGST:
Under GST, IGST is a tax levied on all Inter-State supplies of goods and/or services and will be governed by the IGST Act. IGST will be applicable on any supply of goods and/or services in both cases of import into India and export from India.
GST के अंतर्गत, IGST वस्तुओं और सेवाओं की सभी अंतर-राज्य आपूर्ति पर लगाया जाने वाला कर है और यह IGST अधिनियम द्वारा शासित होता है | IGST भारत में आयात और भारत से निर्यात दोनों मामलों में वस्तुओं और सेवाओं की किसी भी आपूर्ति पर लागू किया जा सकता है ।
50. Payroll:
It refer to the amount of money the employer pays its workers. We often use the term when we are talking about the process of calculating workers' pay and taxes. For example, an accountant may say the following to her husband: “I will be home late tonight. I am doing payroll.”
यह उस राशि का उल्लेख करता है जो employer अपने कर्मचारियों को भुगतान करता है। जब हम श्रमिकों के वेतन और करों की गणना की प्रक्रिया के बारे में बात कर रहे होते हैं तो हम अक्सर इस शब्द का उपयोग करते हैं।
51. TDS:
TDS full form is Tax Deducted at Source. Under this mechanism, if a person (deductor) is liable to make payment to any other person (deductee) will deduct tax at source and transfer the balance to the deductee.
आपकी इनकम का कुछ भाग (प्रतिशत) आपको इनकम प्रदान करने वाली संस्था द्वारा काटा जाता है उसे ही टीडीएस कहते हैं। जो संस्था इनकम का कुछ प्रतिशत काटती है उस पैसे को सरकार के खाते में जमा कर देती है। इसे Tax Deducted at Source कहते है |
52. TCS:
Tax collected at source (TCS) is the tax payable by a seller which he collects from the buyer at the time of sale. Section 206C of the Income-tax act governs the goods on which the seller has to collect tax from the purchasers
Tax collected at source (TCS) विक्रेता द्वारा एक payable tax होता है जिसे वह बिक्री के समय खरीदार से एकत्र करता है। Income-tax act के Section 206C उन वस्तुओं को नियंत्रित करती है जिन पर seller को purchasers से tax एकत्र करना होता है
53. VAT:
A value-added tax (VAT) is collected on a product at every stage of its production during which value is added to it, from its initial production to the point of sale.
किसी product पर उसके उत्पादन के प्रत्येक चरण में value-added tax (वैट) एकत्र किया जाता है, जिसके दौरान उसके प्रारंभिक उत्पादन से बिक्री के बिंदु तक मूल्य जोड़ा जाता है।
54. Octroi
Octroi is a kind of charge or tax, which is collected by the state government on those goods that have been bought into the city/state for the purpose of personal use and sale. The charges on the items are generally levied after on the weight, value and total number of goods.
Octroi याने चुंगी एक प्रकार का शुल्क या tax है, जो राज्य सरकार द्वारा उन सामानों पर एकत्र किया जाता है जिन्हें व्यक्तिगत उपयोग और बिक्री के उद्देश्य से शहर/राज्य में खरीदा गया है। वस्तुओं पर शुल्क आम तौर पर वजन, मूल्य और माल की कुल संख्या के बाद लगाया जाता है।
55. Carriage
Carriage refers to the cost of transporting goods into a business from a supplier, as well as the cost of transporting goods from a business to its customers.
Carriage, supplier द्वारा व्यवसाय में माल के परिवहन की लागत को संदर्भित करता है और साथ ही साथ व्यवसाय से अपने ग्राहकों तक माल के परिवहन की लागत को भी सम्मिलित करता है |
56. Direct Tax:
A direct tax is a tax that a person or organization pays directly to the entity that imposed it. An individual taxpayer, for example, pays direct taxes to the government including Income Tax.
प्रत्यक्ष कर याने direct tax एक ऐसा tax है जो एक व्यक्ति या संगठन सीधे उस संस्था को देता है जिसने इसे लगाया है। उदाहरण के लिए, सरकार को direct tax pay करना जैसे Income Tax.
57. Indirect Tax:
Indirect taxes are typically added to the prices of goods or services. Sales tax, value-added tax, excise tax, and customs duties are examples of indirect taxes.
Indirect taxes आमतौर पर वस्तुओं या सेवाओं की कीमतों में जोड़े जाते हैं। जैसे Sales tax, value-added tax, excise tax, and customs duties
58. Point of Sale:
A point of sale (POS) is a place where a customer executes the payment for goods or services and where sales taxes may become payable
point of sale (POS) एक ऐसा स्थान होता है जहां ग्राहक वस्तुओं या सेवाओं के लिए भुगतान करता है और जहां sales taxe, payable होता है
59. Prepaid Expense:
Prepaid expenses are future expenses that are paid in advance. On the balance sheet, prepaid expenses are first recorded as an asset. After the benefits of the assets are realized over time, the amount is then recorded as an expense.
Prepaid expenses भविष्य के खर्च हैं जिनका भुगतान अग्रिम रूप से किया जाता है। बैलेंस शीट पर, प्रीपेड खर्चों को पहले एक paid in advance के रूप में दर्ज किया जाता है। समय के साथ assets के लाभों का एहसास होने के बाद, amount को expense के रूप में दर्ज किया जाता है।
60. Wages:
Wages are compensation for an employee's personal services, whether paid by check or cash
वेतन एक कर्मचारी की व्यक्तिगत सेवाओं के लिए मुआवजा है, चाहे चेक या नकद द्वारा भुगतान किया गया हो
61. Salary
Salary is a fixed amount of money or compensation paid to an employee by an employer in return for work performed. Salary is commonly paid in fixed intervals, for example, monthly payments of one-twelfth of the annual salary.
वेतन एक निश्चित राशि या नियोक्ता द्वारा किसी कर्मचारी को किए गए काम के बदले में दिया गया मुआवजा है। वेतन का भुगतान आमतौर पर निश्चित अंतराल में किया जाता है, उदाहरण के लिए, वार्षिक वेतन के बारहवें हिस्से का मासिक भुगतान।
62. Receipts:
It is a document issued by the receiver of cash to the giver of cash acknowledging the cash received voucher.
रसीद एक दस्तावेज है जो यह स्वीकार करता है कि किसी व्यक्ति को माल की बिक्री या सेवा के प्रावधान के बाद भुगतान में धन या संपत्ति प्राप्त हुई है।
63. Ledger:
The book of final entry where accounts lie.
final entry की पुस्तक जहां खाते होते हैं।
64. Vouchers:
A voucher is an internal document describing and authorizing the payment of a liability to a supplier.
वाउचर एक internal document होता है जो supplier को liability के भुगतान का वर्णन और उसे अधिकृत करता है।
65. Journal entries:
A daily record of transaction.
लेनदेन का एक दैनिक रिकॉर्ड।
66. Profit:
Profit is a term that often describes the financial gain a business receives when revenue surpasses costs and expenses.
लाभ एक ऐसा शब्द है जो अक्सर एक व्यवसाय को प्राप्त होने वाले वित्तीय लाभ का वर्णन करता है जब राजस्व लागत और व्यय से अधिक हो जाता है।
67. Loss:
A loss is an excess of expenses over revenues, either for a single business transaction or in reference to the sum of all transactions for an accounting period.
एक हानि राजस्व पर व्यय की अधिकता है, या तो एक व्यापार लेनदेन के लिए या एक लेखा अवधि के लिए सभी लेनदेन के योग के संदर्भ में।
68. Balance Sheet:
A balance sheet is a financial statement that reports a company's assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity.
बैलेंस शीट एक वित्तीय विवरण याने financial statement होता है जो कंपनी के assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity को रिपोर्ट करता है।
69. Trial Balance:
A trial balance is a bookkeeping worksheet in which the balance of all ledgers are compiled into debit and credit account column totals that are equal
ट्रायल बैलेंस एक बहीखाता कार्यपत्रक है जिसमें सभी लेज़रों के बैलेंस को डेबिट और क्रेडिट अकाउंट कॉलम में संकलित किया जाता है जो बराबर होते हैं
70. Profit and Loss Statement:
The term profit and loss (P&L) statement refers to a financial statement that summarizes the revenues, costs, and expenses incurred during a specified period, usually a quarter or fiscal year.
प्रॉफिट एंड लॉस (पी एंड एल) स्टेटमेंट एक वित्तीय विवरण को संदर्भित करता है जो एक निर्दिष्ट अवधि याने specified period, आमतौर पर एक तिमाही या वित्तीय वर्ष के दौरान किए गए राजस्व याने revenues, लागत और व्यय का सारांश देता है।
Groups in Tally ERP 9
What are Groups in Tally ERP 9 ?
टैली ईआरपी 9 में समूह क्या हैं?
The group is a collection of legders of the same natures. Tally software automatically creates 28 groups that are used in the account chart. Out of 28 predefined groups in tally, primary groups are 15, and the sub-groups are 13. The different types of groups are as follows:
Groups समान प्रकृति के legders का एक संग्रह होता है। टैली सॉफ्टवेयर स्वचालित रूप से 28 group बनाता है जो अकाउंट चार्ट में उपयोग किए जाते हैं। टैली में 28 पूर्वनिर्धारित group में से, प्राथमिक group 15 हैं, और sub-groups 13 हैं। विभिन्न प्रकार के समूह इस प्रकार हैं:
Primary Group
Sub Group
Primary Groups
This group is the main group. Primary groups are at the top of the hierarchy. Among 15 groups, 6 groups are profit and loss a/c items, and 9 groups are balance sheets items.
यह group मुख्य group होते है। प्राथमिक समूह hierarchy के शीर्ष पर हैं। 15 समूहों में, 6 समूह लाभ और हानि खाते हैं, और 9 समूह बैलेंस शीट आइटम हैं।
List of Primary Group in Tally

Sub Groups
This group is part of the primary group. It can be divided into 13 groups.
List of Sub Group in Tally

Following are the Ledgers with their Groups
नीचे लेजर हेड और उसके संबंधित समूह का विवरण दिया गया है




Accounting Voucher
Go to Gateway of Tally > Accounts Info. or Inventory Info. > Voucher Type > Create. Enter the Name of the voucher.
There are mainly the following types of accounting vouchers in Tally –
टैली में मुख्य रूप से एकाउंटिंग वाउचर निम्न प्रकार के होते है –
Contra Voucher
Payment Voucher
Receipt Voucher
Journal Voucher
Sales Voucher
Purchase Voucher
Credit Note Voucher
Debit Note Voucher
Contra Voucher
When we do any transaction with the bank, then we use contra voucher. We use this voucher when we deposit cash in the bank or withdraw cash. Contra vouchers are used even when the funds are transferred from one bank to another. F4 key is used to use this voucher.
जब हम बैंक से कोई लेनदेन करते है तब contra voucher का प्रयोग करते है ! इस वाउचर का प्रयोग हम तब करते है जब हम बैंक में cash जमा करवाते है या फिर cash withdraw करते है ! फण्ड को एक बैंक से दुसरे बैंक में ट्रान्सफर करने पर भी contra वाउचर का use किया जाता है ! इस वाउचर का प्रयोग करने के लिए F4 key का use किया जाता है !
Contra Vouchers are mainly used in three types of transactions
contra वाउचर का प्रयोग मुख्य रूप से तीन प्रकार के transaction में किया जाता है
Cash Deposit in Bank
Cash Withdraw from Bank
Bank to Bank Transfer
Payment Voucher
We use the payment voucher when we have to make payment to any party or pay any kind of expenses, whether this payment is done in cash or through bank, then this voucher is used. Is ! F5 key is used to use the payment voucher
भुगतान वाउचर का प्रयोग हम तब करते है जब हमें किसी पार्टी को payment करना हो या फिर किसी भी प्रकार के खर्चे का भुगतान करना हो , चाहे यह भुगतान cash में किया जाता है या फिर bank के माध्यम से , तब इस वाउचर का प्रयोग किया जाता है ! payment वाउचर का use करने के लिए F5 key का प्रयोग किया जाता है !
Payment voucher will be used for the following types of transactions
निम्न प्रकार के लेनदेनो के लिए payment voucher का प्रयोग किया जायेगा –
1. किसी पार्टी को भुगतान करना ( Cash / Bank Paid to Ram )
2. किराया दिया ( Rent Paid )
3. वेतन दिया ( Salary Paid )
Receipt Voucher
We use this voucher when we have money! Now whether this money comes to us in cash or through the bank, receipt voucher will be used in both the cases! F6 is used to use this voucher.
इस वाउचर का प्रयोग हम तब करते है जब हमारे पास पैसा आता है ! अब चाहे यह पैसा हमारे पास cash में आता हो या फिर bank के माध्यम से दोनों ही स्थिति में receipt voucher का use किया जायेगा ! इस वाउचर का प्रयोग करने के लिए F6 का प्रयोग किया जाता है !
The following transactions are done in the receipt voucher –
निम्न लेनदेनो को receipt वाउचर में किया जाता है –
1. On receipt of money for goods sold on credit to any person or party.
किसी व्यक्ति या पार्टी को उधार में बेचे गए माल का पैसा प्राप्त होने पर !
2. On selling any property of the business in cash!
व्यवसाय की कोई सम्पति नगद में बेचने पर !
3. On receipt of commission!
कमीशन प्राप्त होने पर !
Journal Voucher
This voucher is mainly used for adjustment. That is, the entries that are not made in other vouchers are entered in the journal voucher only. F7 key is used to use this voucher.
इस वाउचर का प्रयोग मुख्य रूप से adjustment के लिए किया जाता है ! यानि की जो एंट्रीज़ अन्य वाउचर में नहीं की जाती है उसकी entry जर्नल वाउचर में ही की जाती है ! इस वाउचर का प्रयोग करने के लिए F7 key का प्रयोग किया जाता है !
The following types of transactions will be entered in this voucher –
निम्न प्रकार के लेनदेनो की entry इस वाउचर में की जाएगी –
1. Entry of interest on loan!
लोन पर ब्याज की इंट्री !
2. Buying and selling a property on credit!
क्रेडिट पर किसी सम्पति को खरीदना और बेचना !
3. Charging Depreciation on Property!
सम्पति पर ह्रास ( Depreciation ) चार्ज करना !
4. Entry of Bills Receivable and Bills Payable etc.!
Bills Receivable और Bills Payable की इंट्री आदि !
Sales Voucher
We use this voucher when any goods or items are sold by us, whether it is in credit or in cash. The F8 key is used to use the sales voucher.
इस वाउचर का प्रयोग हम तब करते है जब हमारे द्वारा कोई माल या वस्तु बेचीं जाती है , चाहे यह उधार में हो या फिर cash में ! sales वाउचर के प्रयोग के लिए F8 key का use किया जाता है !
Example :
1. Sold goods worth 1000 to Ram!
राम को 1000 का माल बेचा !
2. Sold goods worth 5000 in cash!
नगद में 5000 का माल बेचा !
3. Sold machinery for cash, etc.
नगद में मशीनरी बेचीं, आदि !
Purchase Voucher
Using this voucher, whatever goods or goods we buy for business, whether we buy it in cash or in credit, all transactions will be entered in the purchase voucher! F9 key is used to use this voucher.
इस वाउचर का प्रयोग व्यवसाय के लिए जो भी सामान या गुड्स purchase करते है , चाहे वह हम नगद में खरीदते है या फिर उधार में , सभी लेनदेन की entry purchase voucher में की जाएगी ! इस वाउचर का प्रयोग करने के लिए F9 key का प्रयोग किया जाता है !
Example :
1. Bought cash goods from Shyam!
श्याम से नगद माल ख़रीदा !
2. Bought cash goods from Shyam
फर्नीचर ख़रीदा !
3. Bought machinery!
मशीनरी खरीदी !
Types of Accounts
There are mainly three types of accounts in accounting: real, personal and nominal accounts
लेखांकन(Accounting) में मुख्य रूप से तीन प्रकार के खाते होते हैं: वास्तविक(Real), व्यक्तिगत(Personal) और नाममात्र खाते(Nominal), व्यक्तिगत

Real Account
Real Account is mainly related with Assets rather it can be fixed or current.
Ex. Car, building, cash, etc
रियल अकाउंट मुख्य रूप से एसेट्स से संबंधित होता है बल्कि इसे फिक्स या चालू किया जा सकता है। भूतपूर्व। कार, भवन, नकद, आदि
Under this account, all types of purchases and sales related to business are entered.
इस खाते के अंतर्गत ब्यापार में होने वाले समस्त प्रकार की खरीद बिक्री से सम्बन्धित इंट्री की जाती है
इस खाते के निम्न दो नियम है

1.ब्यापार में आने वाला Dr. 2.ब्यापार में जाने वाला Cr.

Personal Account
Personal Account is mainly related with person, company, institution, or any individual name
व्यक्तिगत खाता मुख्य रूप से व्यक्ति, कंपनी, संस्था, या किसी व्यक्ति के नाम से संबंधित है
Under this account, entry related to any person, organization or bank is made. it has two rules
इस खाते के अंतर्गत किसी ब्यक्ति , संश्था या बैंक से सम्बन्धित एंट्री की जाती है .
इसके दो नियम है

1. पाने वाला ब्यक्ति ऋणी Dr
2. देने वाला ब्यक्ति धनी Cr.




Nominal Account
Nominal Account is mainly related with all types expenses and losses as well as income and gain
नाममात्र का खाता मुख्य रूप से सभी प्रकार के खर्चों और हानियों के साथ-साथ आय और लाभ से संबंधित है
Under this account, entry is made related to all types of income and expenditure,
इस खाते के अंतर्गत समस्त प्रकार के आय तथा ब्यय से सम्बन्धित इंट्री की जाती है
इसके निम्न दो नियम है

1.आय या लाभ धनी Cr.
2.ब्यय या हानि ऋणी Dr.




Some Transactions
Sold Goods of Rs.45,000 to Mohan & Company on credit
Purchase Goods of Rs.10000 from Ashish & Company on credit
Purchase Raw Material of Rs.5000 by cash
Paid for Computer Repair Rs.700
Paid Auto charges Rs.200
Paid Tea & Snacks bill Rs.500
Paid Rs.4000 for Office
Paid Labour charges Rs.1500
Paid Xerox charges Rs.200
Paid Transportation charges Rs.900
Paid Electric bill of Rs.1500
Received cheque of Rs.45000 from Raju & Company
Paid cheque of Rs.10.000 to Ashish & Company
Deposit Rs.15000 in SBI
Withdrawal of 5000 from SBI
Started Business of RS.20.000
Paid Legal fees Rs.2000
Paid Office Cleaning charges Rs.1000
Purchase Water Cooler of Rs.14,000
Paid Office rent Rs.9000
Paid Driver & Cleaner salary Rs.8000
Purchase Ceiling fan of Rs.5000 for Office
Paid Courier charges of Rs.500
Paid Mobile charges of Rs.600
Paid Rs.800 for Office Refreshment Party
Purchase 3 Computers for Office use @ of 25,000 cash computer & printer Rs.12,000 from Computer Workshop on credit
Received Interested of Rs.900 on bank account
Paid Loan instalment of Rs.15,000
Paid Water bill of Rs.1000
Purchase New Furniture for Office Rs.25.000
Create Company

Create Ledgers
Create a new company – Suraj Pvt. Ltd. & create following Ledgers.

Create a new company – Pavan Pvt. Ltd
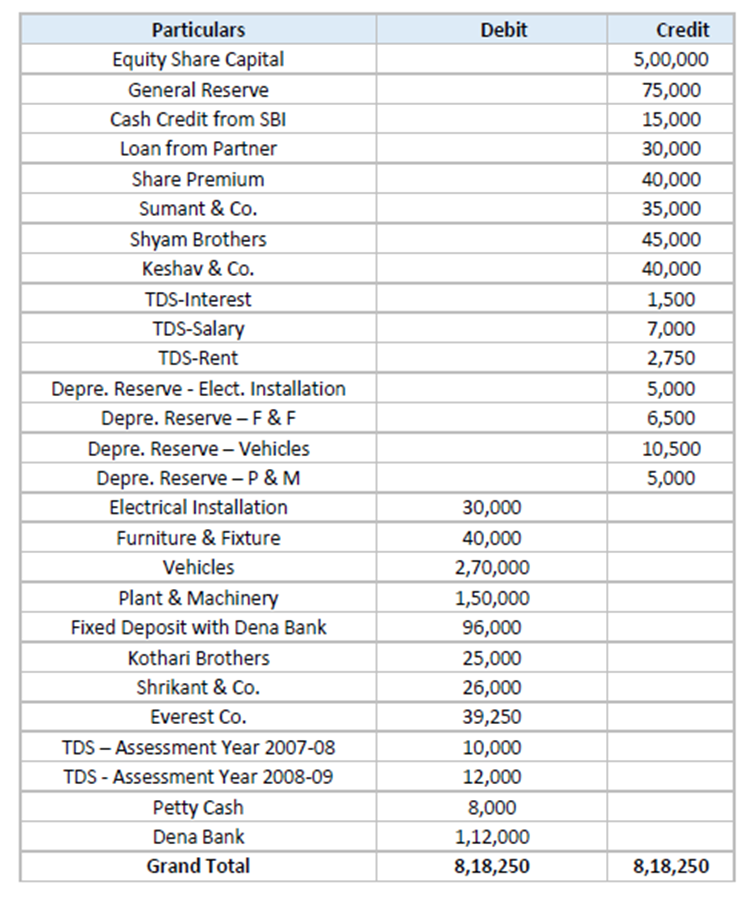
Create a new company – Ledger Creation


Create a new company – Surag Pvt. Ltd

Solve Transactions
ACCOUNTS ONLY
1. Mr Sharma

2. Solve Transactions – Ms Rima

3. Solve Transactions – Mr. Ravi

4. Solve Transactions – Mr. Nikhil

5. Solve Transactions – Mr. Mahesh


6. Solve Transactions – Petty Cash 1


7. Solve Transactions – Petty Cash 2

8. Shubhangi Pvt Ltd.


9. Jeevan Daya Traders





10. Mother Pvt. Ltd.







13. M/S Akbar Ali Money Lander




BANK RECONCILIATION PROBLEM (Accounts Only)



Solve Transactions
COST - CENTER PROBLEMS (Accounts Only)




Solve Transactions
INVENTORY PROBLEMS
Problem 1. Bhojwani Trading Company





Problem 2. Hari Om Rice Mill






Problem 3. Gopal Anna Bhandar

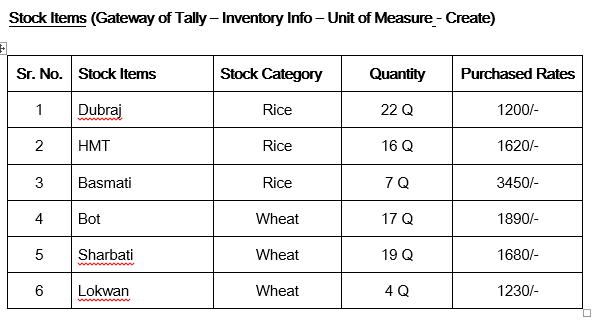

Problem 4. Padma Cloth Stores
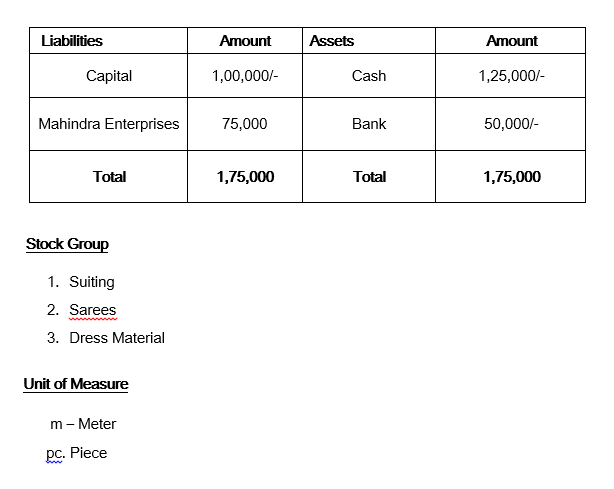

Solve Transactions
PROBLEM ON MULTI-CURRENCY PROBLEM
Create Company with Inventory
Press F11
Accounting Feature
Allow Multi-Currency
Enter-Enter-Accept
Accounts Info
Currencies
Create Symbol $(Formal Name Dollar)
Enter-Enter-Accept-Esc
Rate of Exchange
Std Rate Selling Specified Rate Buying Specified Rate
Rs.73/$ Rs.75/$ Rs. 70/$
Enter-Enter
Inventory Info
Stock Group-Create-Computer
Enter-Enter-Accept-Esc
Unit of measure-Create-No. (Number)
Enter-Enter-Accept-Esc
Stock Item-Create
1. HP (Under Computer & Unit-No) – Quantity 50 – Rate 11,425/-
2. ACCER (Under Computer & Unit-No) - Quantity 50 – Rate 10,667/-
Enter-Enter-Accept-Esc
Account Info
Ledger-Create
1. Sharma & Co. (Sundry Creditor)
2. Sagar & Co. (Sundry Debtor)
3. Sales (Sales Account)
4. Purchase (Purchase Account)
Escape-Escape
Accounting Voucher
Purchase Voucher F9
Party Name-Sharma & Co,
Purchase Ledger - Purchase
Enter
1. Item-HP Computer-Rate $150
Enter-Enter
2. Item-ACCER Computer-Rate $140
Enter-Enter-Accept
Sales Voucher F8
Party Name-Sagar & Co.
Sales Ledger - Sales
Enter
1. Item-HP Computer – Quantity 10 - Rate $209
Enter-Enter
2. Item-ACCER Computer – Quantity 10 - Rate $196
Enter-Enter-Accept

Comments